Getting Started: Herpes Virus vs HPV
If you’re here, it’s likely because you’ve heard of both the herpes virus and human papillomavirus (HPV), but you might be unsure about their differences, how they impact your health, and how to properly address them. The sheer amount of conflicting information available online can make navigating these two viral infections a bit confusing. But, don’t worry, you’re in the right place to clear up any misunderstandings. In this article, I will take you through the key differences between the herpes virus and HPV, offering detailed insights into their symptoms, causes, transmission methods, potential risks, and available treatments.
Discover our natural products store: SALE SUPRA
Discover the power of PAPILLEX
Both the herpes virus and HPV are highly prevalent viruses, yet they affect the body in fundamentally different ways. Whether you’re dealing with one of these infections yourself or you’re simply trying to better understand them, you’ll find this guide informative and easy to digest. In addition to discussing treatment options, I’ll also touch on Papillex, a supplement designed to support those dealing with HPV infections.
By the end of this article, you’ll not only know how these viruses differ but also how to take control of your health, whether you’re looking for symptom relief or preventative measures.
What is the difference between the herpes virus and HPV?
The herpes virus causes painful outbreaks like cold sores and genital herpes, while HPV is a group of viruses that can lead to warts or increase the risk of certain cancers, including cervical cancer. Herpes Virus vs HPV
Herpes Virus vs HPV: A Comprehensive Comparison
While both the herpes virus and HPV can be spread through sexual contact and are prevalent worldwide, they differ significantly in how they affect the body and the diseases they cause. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone looking to prevent, manage, or treat these infections.
Herpes Virus
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is responsible for two main types of infections:
- HSV-1 (Oral Herpes): This virus is most commonly associated with cold sores or fever blisters that appear on or around the mouth, but it can also cause genital herpes through oral-genital contact.
- HSV-2 (Genital Herpes): Primarily associated with genital herpes, HSV-2 is transmitted through sexual contact. While HSV-2 is primarily linked to genital outbreaks, it can also occasionally affect the mouth.
Herpes infections are highly contagious, and the virus can be transmitted even when symptoms aren’t visible. Once contracted, the virus remains in the body and can become dormant in nerve cells, only to reactivate later—usually during times of stress, illness, or a weakened immune system. Herpes Virus vs HPV
Symptoms of Herpes:
- Cold sores or blisters: Usually found around the mouth for HSV-1 or on the genitals for HSV-2.
- Itching, tingling, or burning: Often felt before an outbreak appears.
- Painful urination: This can occur when genital sores are present.
- Flu-like symptoms: This includes fever, muscle aches, and swollen lymph nodes, especially during the first outbreak.
The symptoms may not always be present, and the virus can remain dormant in the body, only to be triggered by specific factors such as stress or a weakened immune system. Herpes Virus vs HPV
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
HPV is a collection of more than 200 related viruses. Some strains of HPV are low-risk and cause benign growths like warts, while others are high-risk and can lead to cancers such as cervical, anal, and throat cancers.
What makes HPV unique is that the majority of infections are asymptomatic. This means that many people carry the virus without ever showing any symptoms. For this reason, HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) in the world. Herpes Virus vs HPV
Symptoms of HPV:
- Genital warts: Small growths or lumps that appear on the genital, anal, or oral areas.
- Changes in cervical cells: High-risk strains of HPV may cause abnormal changes in cervical cells, which can be detected through a Pap smear. These changes, if untreated, can lead to cervical cancer.
- Throat lesions: In some cases, HPV may cause warts or other lesions in the throat. Herpes Virus vs HPV
Most HPV infections will resolve on their own, but certain strains, particularly high-risk ones, can persist and potentially lead to more serious health issues like cancer. Because HPV often shows no symptoms, regular screenings, such as Pap smears for women, are crucial for early detection and prevention. Herpes Virus vs HPV
How Herpes Virus and HPV Are Transmitted
While both the herpes virus and HPV can be spread through sexual contact, their methods of transmission and potential for contagion are different. Understanding how these viruses are transmitted can help you take preventive measures and reduce the risk of spreading them. Herpes Virus vs HPV
Transmission of Herpes Virus
Herpes is highly contagious, and the primary mode of transmission is through direct skin-to-skin contact with someone who has the virus. This can include: Herpes Virus vs HPV
- Kissing: If someone with oral herpes (HSV-1) kisses you, the virus can spread to your lips.
- Sexual contact: Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 can be spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
- From infected surfaces: While not as common, herpes can be transmitted through shared items like towels, razors, or eating utensils.
- Mother to child: A pregnant woman with genital herpes can pass the virus to her baby during childbirth, which can be dangerous for the newborn.
Even without visible sores or symptoms, the herpes virus can still be transmitted from one person to another, making it highly contagious. Herpes Virus vs HPV
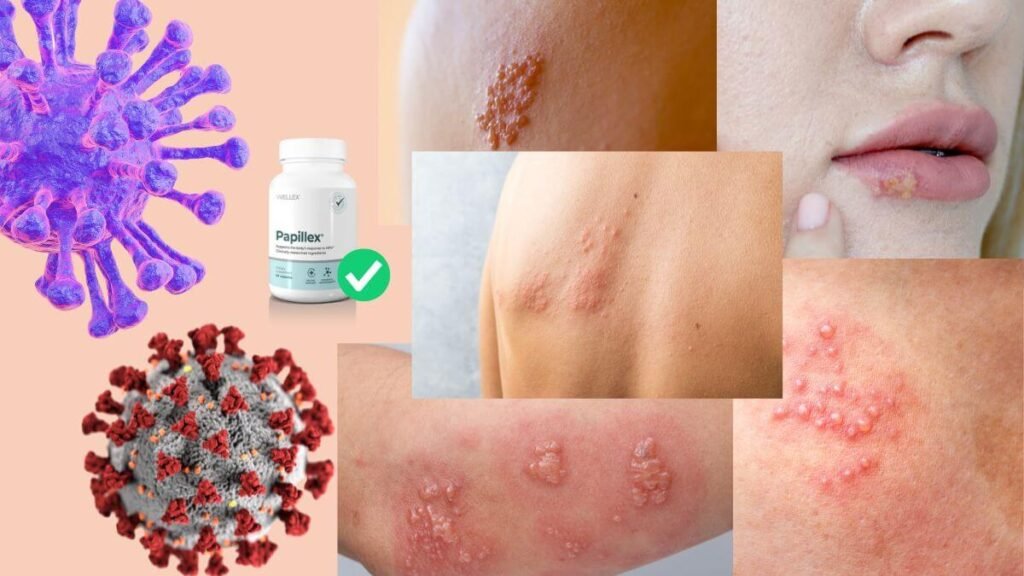
Transmission of HPV
HPV is primarily spread through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. However, HPV can also be spread through skin-to-skin contact, even if no sexual intercourse takes place. Some of the key transmission routes for HPV include: Herpes Virus vs HPV
- Sexual contact: The most common way HPV is spread is through sexual activity. This includes both genital and oral sex.
- Non-sexual skin-to-skin contact: HPV can be transmitted by touching an infected area, which is why even non-sexual contact can sometimes spread the virus.
- Mother to child: Although rare, HPV can be passed from a mother to her baby during childbirth, especially if the mother has genital warts.
Unlike herpes, HPV can sometimes be asymptomatic, meaning a person can carry and spread the virus without knowing it. This is one reason why it’s so widespread—most people with HPV never realize they have it until complications arise. Herpes Virus vs HPV
Treatment Options for Herpes Virus and HPV
Currently, there is no cure for either the herpes virus or HPV, but both can be managed with the right treatment. Here’s an overview of the options available for managing both viruses: Herpes Virus vs HPV
Treatment for Herpes Virus
- Antiviral medications: Drugs like acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir can help reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks by inhibiting the virus’s ability to replicate.
- Topical treatments: Over-the-counter creams and ointments can help soothe sores and relieve itching during an outbreak.
- Pain management: Non-prescription pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help ease the discomfort associated with herpes outbreaks.
Although these treatments can’t cure herpes, they help manage the symptoms and reduce the chance of transmission. Herpes Virus vs HPV
Treatment for HPV
- Vaccination: The HPV vaccine (Gardasil) can protect against the most common and high-risk strains of the virus. It’s recommended for both boys and girls, ideally before they become sexually active.
- Genital warts treatment: Warts caused by HPV can be treated with topical medications, cryotherapy (freezing), or surgical removal.
- Cervical screening: Regular Pap smears for women can detect changes in cervical cells caused by HPV. Early detection of abnormal cells can prevent the development of cervical cancer.
While HPV often resolves on its own, certain strains can lead to more severe health issues. Regular screenings and vaccinations can significantly reduce the risks associated with this virus. Supplements like Papillex, formulated to support immune function, can also be used to manage HPV symptoms and help prevent warts from reappearing. Herpes Virus vs HPV
Discover our natural products store: SALE SUPRA
Discover the power of PAPILLEX
The Final Takeaway
Understanding the differences between the herpes virus and HPV is essential for anyone navigating these conditions. While both are common viral infections transmitted primarily through sexual contact, they have distinct symptoms, causes, and long-term effects. The herpes virus causes painful outbreaks, whereas HPV can lead to warts and, in some cases, cancers. Herpes Virus vs HPV
Although neither condition has a cure, both can be effectively managed with the right treatment. Antiviral medications, regular screenings, and vaccines like the Gardasil shot can help mitigate the effects of both viruses. Additionally, using supplements like Papillex can help boost your immune system and manage HPV-related symptoms.
Taking control of your health is key, and now that you have a better understanding of herpes and HPV, you can make informed decisions regarding treatment and prevention. If you suspect you have either of these conditions, consulting with a healthcare professional is always the best first step.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between the herpes virus and HPV?
Herpes causes painful sores and blisters, while HPV can lead to warts or, in some cases, increase the risk of cancers, especially cervical cancer.
2. How is the herpes virus transmitted?
Herpes is transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact, including kissing and sexual activity. It can also spread from contaminated surfaces.
3. Can HPV cause cancer?
Certain high-risk strains of HPV can cause abnormal cell changes that may lead to cancer, particularly cervical, anal, and throat cancers.
4. Is there a cure for herpes or HPV?
There is no cure for either herpes or HPV, but antiviral medications can manage herpes outbreaks, and vaccines and treatments are available for HPV-related issues.
5. How can I prevent HPV?
Vaccination with the Gardasil vaccine can protect against the most harmful strains of HPV. Regular screenings and Pap smears are also essential.
6. Can Papillex help with HPV?
Yes, Papillex is a supplement designed to support immune health and manage HPV symptoms, particularly related to warts and skin lesions.
Image Captions:
- Herpes virus vs HPV: Understanding the key differences and symptoms.
- HPV treatment options: Vaccines and supplements like Papillex.
- Herpes outbreaks: Managing symptoms with antiviral medications.
- Papillex: A natural supplement to support immune health in HPV.
- Preventing cervical cancer with regular Pap smears and HPV vaccination.
- Reducing HPV symptoms and warts with targeted treatments.

I’m an economist with 15 years of experience in strategic planning and a lifelong passion for wellness and natural living. As a self-learner, I created Herbalife Balance to share insights on healthy eating, mindful habits, and an active lifestyle. Tennis enthusiast and nature lover, I believe in balance as a path to well-being. Through this blog, I help others live healthier, more conscious lives.